Inventory Turnover Ratio Explained
What is inventory turnover?
Inventory turnover, also known as stock turnover, indicates the time between when a company purchases an item and when that item is ultimately sold. A completed turnover occurs once the company has sold the item it purchased. Ideal inventory turnover differs for each industry. Companies in industries with rapidly changing products, like fashion or electronics, typically have higher turnover rates. In comparison, those dealing with more durable or long-lasting goods may have lower turnover rates. Inventory planning and management are essential since issues with the supply chain, overstocking and customer demand can all impact turnover.
What is inventory turnover ratio?
Inventory turnover ratio measures the number of times a company “turned over” (i.e., sold and replaced) its inventory in a specific period. It shows how efficiently the business uses its assets and manages its inventory. A higher ratio is preferable as this suggests a company is effectively managing its inventory and not tying up excess capital in unsold goods. A lower ratio indicates a company may have excessive or obsolete inventory and should reevaluate if and how much of that product is needed to satisfy demand. Consistent monitoring of inventory turnover ratio is critical, particularly with high-turnover goods, to ensure adequate supply is available to meet demand and avoid stock-outs.
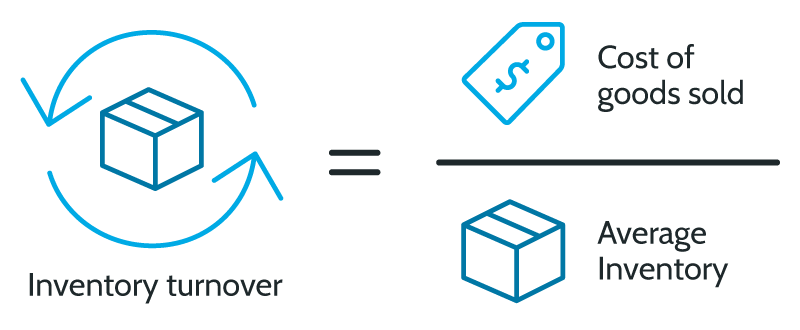
Calculating inventory turnover ratio
To calculate the company’s inventory turnover ratio, you must first identify the average inventory in a certain period. This number can be determined by adding the inventory value at the beginning of the set time period and the end. Then, divide this figure by two. Once the average inventory has been identified, divide the cost of goods sold (COGS) in the same period by the average inventory. COGS is the cost of producing goods the company sells, which is detailed on the company’s income statement. Inventory is usually valued at cost, so analysts use this figure instead of sales. Using average inventory in the calculation counteracts seasonality. Some businesses see drastic inventory fluctuations based on seasonal trends.
Inventory Turnover Calculator
How to use the calculator:
- Input the total Costs of Goods Sold (COGS).
- Input your beginning and ending inventory amounts.
- Click on “Calculate” to produce your results.
Why does inventory turnover matter?
Allows businesses to make better decisions, increasing profits and optimizing efficiency.
For example, slower-selling products may need price adjustments, discounts or discontinuation to avoid unnecessary overhead costs such as storage fees.
Provides key insights to better manage inventory and meet customer demand.
For example, a company may stock more inventory leading up to the holiday season, utilizing the inventory turnover ratio to help plan for these fluctuations in demand.
Offers a valuable metric for benchmarking against competitors or industry standards.
Analyzing your inventory turnover ratio allows you to gauge performance relative to others in similar industries or markets.
What is a good inventory turnover ratio?
An ideal or “good” inventory turnover ratio can vary significantly depending on the industry. The type of products you sell dramatically influences the speed at which stock is replenished, depending on how essential they are, their cost and longevity. Generally, a higher inventory turnover ratio is considered better because it signifies a business is efficiently managing its inventory. For example, an inventory ratio between two and six indicates a company’s restock rates match its sales cycle—the amount of inventory is just right to meet demand.
Generally, a good inventory turnover ratio balances having enough inventory to meet customer demand while avoiding excessive carrying costs. A ratio that’s too high may result in stockouts and lost sales, while a ratio that’s too low may lead to carrying excessive inventory with associated costs.
How to improve inventory turnover ratio
If your inventory turnover ratio is low, conducting a comprehensive assessment of your inventory management processes is good practice. A likely cause for a low ratio is decreased or insufficient demand. To enhance this metric, it is crucial to implement strategies to bolster customer demand and optimize the efficiency of your inventory turnover processes.
What can you do to boost sales? Could you alter your marketing strategy to promote the company’s brand and products better? Could you explore other marketplaces to extend your reach?
Your competitors might be selling specific products more effectively. If their prices are lower, consider adjusting your pricing. If necessary, discontinue products that are performing poorly. Incorporating automation into your inventory management process is another effective way to streamline your supply chain and speed up inventory turnover. Easy access to accurate data from all your sales channels enables you to effectively receive inventory and move goods to the right place at the right time. Read more about the inventory management services SPS provides here.
Can inventory turnover ratio be too high?
Yes, if your inventory turnover ratio is too high, the company may be at risk of shortages and stockouts due to insufficient inventory.
When your inventory supply is too low, the company will experience problems whenever there is a spike in demand or an issue with the supply chain. Waiting for new stock takes time, and sales opportunities will only be recovered if the business can meet consumer demand.
Fortunately, this is a lesser problem than scaling down inventory due to a low ratio. Simply alter your ordering cycle and increase purchase amounts to balance inventory with demand to help avoid stockouts.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is a good inventory turnover ratio?
How do you calculate inventory turnover ratio?
Is a high inventory turnover ratio good?
Inventory planning with SPS Commerce
Are you interested in turning your sales and community data into powerful insights? SPS Commerce gives you the power to transform your inventory planning process and ensure you always have products in the right place at the right time. Our full-service approach provides real-time insights into product demand, improved operational efficiency and a team of dedicated experts ready to help you deliver the positive experience your customers demand.
For more information, chat with our expert team today.