A complete guide to data standardization
Standardization is a fundamental component of data management for businesses. Data standardization enhances data quality by distinguishing between false and accurate information. It also fosters seamless communication and collaboration between companies.
In this article, SPS Commerce explains what data standardization is, why it’s important and how to develop a data standardization strategy.
Data standardization: what is it & how does it work?
Data standardization is the process of sorting and transforming data, breaking it down into a single, unified format that can be easily processed by computers. This is a common challenge, especially in retail, with products and services often divided into unique groups and classes, with different units and values across suppliers and retailers.
For example, suppliers and retailers exchange a variety of different types of data elements, such as SKU number, price, weight, dimensions, color and more. One retailer might label a black shirt in their system “BLK” while another uses “BLACK.” Data standardization allows these businesses to speak a common language.
For example, suppliers and retailers exchange a variety of different types of data elements, such as SKU number, price, weight, dimensions, color and more. One retailer might label a black shirt in their system “BLK” while another uses “BLACK.” Data standardization allows these businesses to speak a common language.
Without data standardization, the role of computers and data analysts is much more difficult, as they must understand the individual format and context of each piece of information as well as what that information represents.
Why is data standardization important?
Data standardization is essential as it allows the sharing and access of consistent and unified streams of data between different businesses and systems, without additional complications or conversions. This makes it easier for data analysts to sift through the right pieces of information quickly and efficiently.
Standardized data also improves a company’s ability to make decisions, as all information acquired will be of greater accuracy, limiting the risk of human error or discrepancies caused by manually comparing data.
Therefore, predictions about the future (like demand forecasts for procurement) will be more accurate, increasing confidence among key decision-makers.
What are the benefits of data standardization?
There are several key benefits to data standardization that make the process valuable for any business, including:
Reduced costs: Companies that lack data standardization often encounter errors that lead to inaccurate business projections, resulting in over-purchasing stock or being unable to meet demand.
Improved productivity: More accurate and detailed data helps businesses better understand company performance metrics and where to address areas of inefficiency, increasing productivity by reducing guesswork and waste. Standardized data makes it possible to automate reports and integrate data into internal BI reports as well.
Enhanced customer acquisition: Businesses can more accurately plan and market products to new customers—as well as improve sales offers and marketing efforts.
Better decision-making: Accurate data empowers businesses to predict what decisions will be most effective, particularly when navigating potential crisis situations, such as the bullwhip effect.
Stronger trading partner relationships: Standardized data allows businesses to provide consistent and reliable information to customers and trading partners, fostering collaboration and trust.
What are the challenges or limitations of data standardization?
Data standardization is crucial. However, its implementation poses many challenges, including:
Incomplete or inaccurate data:
Incomplete or inaccurate data can result in flawed decisions and a wasted data standardization process. The best way to mitigate this risk is to ensure that data is up-to-date, relevant and accurate before undergoing the standardization process.
Inefficient workflows:
A slow or complex workflow within a business or supply chain can result in outdated or inaccurate data. The best way to mitigate this issue is by aligning all stakeholders on an efficient workflow, such as through reporting deadlines or shared data automation platforms.
Complex processes:
There are also obvious challenges in organizing the data itself – with the process of optimizing raw data posing risks in timeliness and accuracy. However, change management tools can negate these challenges by automating the process to save time and avoid errors.
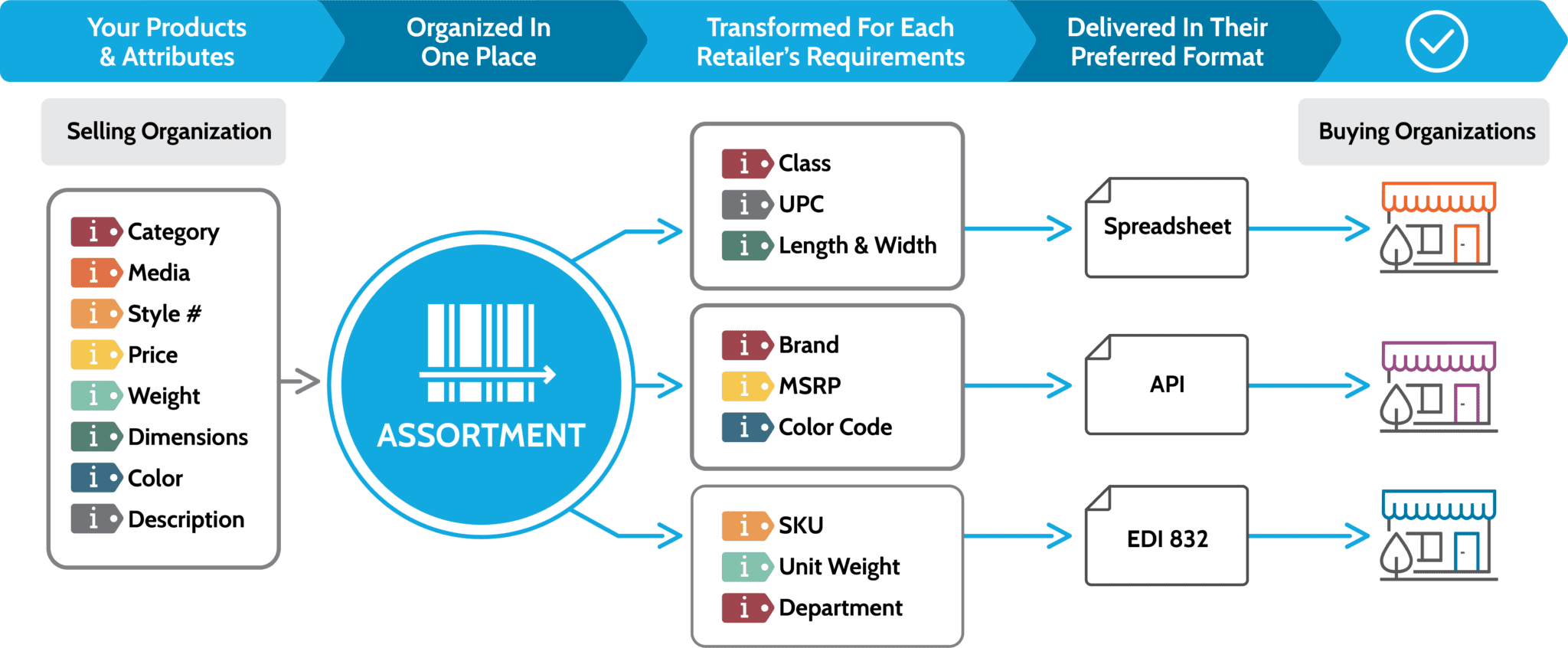
SPS Assortment takes the complexity out of the standardization of product data, transforming and delivering clean data. There’s no need to manage multiple product data systems, custom IT projects, item mapping or messy spreadsheets. Our full-service solution does the heavy lifting!
How to standardize data
There are four key steps to the data standardization process that every company needs to follow to reap the rewards of accurate, standardized data:
Determine data requirements: This process involves determining exactly which format each data entry must be recorded in. For example, dates may be standardized as ‘MM-DD-YYYY’, with global time zones converted into a single digital time, such as Central Standard Time (CST).
Understand data sources: Next, it’s important to review all applicable data sources. This step is used to verify whether the source is reliable and accurate, whether data can be easily converted into the required format, whether the data volume is manageable, and whether these sources are easy to use and access.
Clean data: The term ‘cleaning’ data describes the process of filtering information and removing any incorrect data entries. This can include outdated data, but also data that has been incorrectly entered. For example, a field may require a user’s surname, but instead, their first name has been entered. Removing these inaccurate entries improves the quality of the data set.
Normalize data: This is a key step in developing a final, standardized data set, that involves organizing information to be similar across all fields and creating consistency across entries. It is important to use an automation platform for normalizing data as it reduces the risk of human error – especially across significant data sets – while making the data easier to review and analyze with automated dashboards and reports.
SPS Assortment lets you manage your product data through a single, automated process – taking care of previously manual tasks, so you can focus on what you do best. Our comprehensive solution includes a technology platform, proven processes, and an expert team to help you automate data sharing.
How does data standardization differ from data normalization?
Both data standardization and data normalization processes are used to convert varied data into a single, unified format. However, the difference between the two lies in the types of data sets that they are best applied to.
This makes data standardization the optimal form of data conversion for comparing data from multiple sources – such as all of the partners working across a supply chain. Data normalization, however, is best used for data sets originating from a single source.
Industry-specific considerations for data standardization
Data standardization processes vary by industry.
For example, in the retail industry, retailers collaborate with suppliers to optimize inventory management. Stores may share historical sales data and inventory levels with suppliers, who, in turn, can use this information to ensure timely and efficient replenishment of products. This collaboration relies on the retailer’s sales data for accurate demand forecasting and inventory planning.
Data automation platforms allow users to apply their own rules to the data standardization process—from collecting and recording data in specific formats to generating reports at regular intervals to equip stakeholders with key information.
SPS Assortment lets you manage your product data through a single, automated process – taking care of previously manual tasks, so you can focus on what you do best. Our comprehensive solution includes a technology platform, proven processes, and an expert team to help you automate data sharing.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Q: What Is the purpose of data standardization?
A: The purpose of data standardization is to transform data into a single, unified format. This helps maintain data quality and makes it easier to identify errors or eliminate extraneous data. Ultimately, standardization equips decision-makers with the most accurate picture of their environment and performance.
Q: What are the four key aspects of data standardization?
A: There are four key aspects to consider in data standardization:
- The reliability, accuracy and accessibility of the data source
- Ease of converting the data
- Volume of data and how manageable it is
- Data entry points are clearly defined and easy to use
Q: What are some examples of data standardization?
A: There are many examples of data standardization. One is the conversion of all temperature measurements into degrees Fahrenheit for easier analysis. Another involves changing units of measure to metric, such as converting pounds to kilograms or feet to meters, to ensure consistency across data sources and analyses.